Medieval History / Mughal Sultanate
Mughal Empire Rulers and their History in Chronological Order
Babur is the founder of Mughal empire in India. If we see the Mughal empire rulers list, the period of their rule can be
divided into two phases. The first phase is from 1526 to 1707. It was the golden period of Mughal rule in India starting from Babur to
Aurangzeb. The second phase is from 1707 to 1857. In the second phase, the Mughal dynasty rulers after Aurangzeb
were only namesake kings without having any significant achievement. Timur is an ancestor of Mughal empire rulers in India.
Mughal Empire Rulers Timeline from 1526 to 1857
Below is the list of Mughal empire rulers in order with years showing both six famous Mughal emperors and the namesake later Mughal emperors.
| Sl. No. |
Name of the Emperor |
Period of Reign |
| 1 |
Babur |
1526-1530 |
| 2 |
Humayun |
1530-1540 and 1555-1556 |
| 3 |
Akbar |
1556-1605 |
| 4 |
Jahangir |
1605-1627 |
| 5 |
Shah Jahan |
1628-1658 |
| 6 |
Aurangzeb |
1658-1707 |
| 7 |
Muhammad Azam Shah |
March 1707 - June 1707 |
| 8 |
Bahadur Shah I or Shah Alam I |
1707-1712 |
| 9 |
Jahandar Shah |
1712-1713 |
| 10 |
Farrukhsiyar |
1713-1719 |
| 11 |
Rafi ud-Darajat |
February 1719 - June 1719 |
| 12 |
Shah Jahan II or Rafi ud-Daulah |
June 1719 - September 1719 |
| 13 |
Muhammad Shah or Sada Rangila |
1719-1748 |
| 14 |
Ahmad Shah Bahadur |
1748-1754 |
| 15 |
Alamgir II |
1754-1759 |
| 16 |
Shah Jahan III |
1759-1760 |
| 17 |
Shah Alam II |
1760 - July 1788 and October 1788 - 1806 |
| 18 |
Mahmud Shah Bahadur or Shah Jahan IV |
July 1788 - October 1788 |
| 19 |
Akbar II |
1806-1837 |
| 20 |
Bahadur Shah II |
1837-1857 |
Mughal Empire Famous Rulers from Babur to Aurangzeb
The Mughal empire under different rulers saw both ups and downs. During the first phase from 1526 to 1707, it was a golden era of Mughal
rule and six famous Mughal kings ruled India during this period. These Mughal empire rulers in chronological order are Babur, Humayun, Akbar,
Jahangir, Shah Jahan and Aurangzeb.
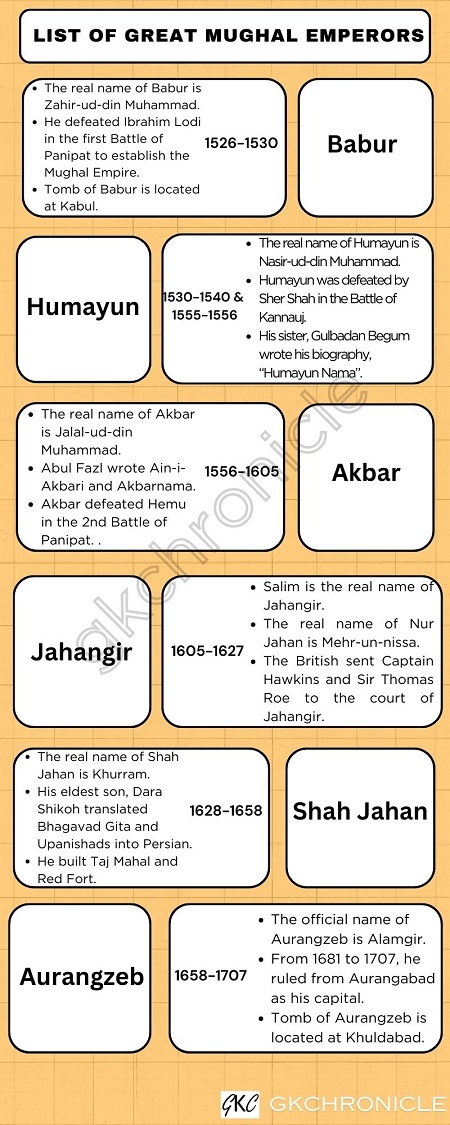
Image taken from royalty-free Canva image gallery for
representative purpose only
Babur (1526-1530)
- Timur had Samarkand (Uzbekistan) as his capital. Over a period, Timurid Empire got divided into small Principalities, namely Samarkand,
Herat, Kabul and Fergana (Babur belongs to this Principality).
- In 1494, Babur became the king of Fergana. As he had a dream of conquering Samarkand, he achieved it in his third attempt. During this
time, his cousin occupied Fergana. But Babur left Fergana to him. The original king of Samarkand recaptured it again.
- Babur then conquered Kabul and ruled from there for 20 years. But Kabul was economically very backward. By this time, two kings from India
invited Babur to conquer India.
The kings, who invited Babur to invade India, were Rana Sangram Singh
of Mewar and Daulat Khan Lodi, who was the governor of Punjab under Lodi dynasty.
- The meaning of Babur is tiger. Babur was born in 1483 AD. The real name of Mughal empire ruler Babur is Zahir-ud-din Muhammad and he is the son of Umar
Sheikh Mirza. Autobiography of Babur, Tuzuk-i-Baburi (or Baburnama) is believed to be one of the best autobiographies.
Babur is known
as prince among the autobiographers. Baburnama is written in 3 chapters, namely (i) Memories of Fergana, (ii) Memories of Kabul and
(iii) Exclusively on India.
- He was in India for 4 years. In every year, he fought a battle
- The first Battle of Panipat was fought between him and Ibrahim Lodi in 1526.
Lodi Ibrahim Lodi was killed and hence Babur established Mughal empire and became the Mughal empire first ruler in India. The rulers of Lodi dynasty,
who ruled before the Mughals, were the last rulers of Delhi Sultanate.
- The Battle of Khanwa was fought in the year 1527 in which Rana Sangram Singh was defeated. Babur declared jihad to fight against
Rana Sangram Singh.
- In 1528, in the Battle of Chanderi (Madhya Pradesh), he defeated a Rajput king Medini Rai (friend of Rana Sangram).
- In 1529, in the Battle of Ghagra or Gogra, Nusrat Shah (son-in-law of Ibrahim Lodi and belonging to Ilyas Shahi dynasty) of Bengal
was defeated.
- On his way to Kabul, Babur died in 1530. The Tomb of Babur is located at Kabul.
- Persian was the court language of Mughals. But Babur's mother tongue was Chagatai Turkish.
Humayun (1530-1540) & (1555-1556)
- The real name of Mughal empire ruler Humayun is Nasir-ud-din Muhammad. In 1540, Humayun was defeated by Sher Shah of Sur
dynasty. For 15 years, he took asylum here and there.
In 1556, he died in an accidental fall from his library. It was his sister
Gulbadan Begum, who wrote Humayunama, his biography.
- Karnavati, widow of Rana Sanga (Sangram Singh) sent a Rakhi to Humayun seeking help during the war with Bahadur Shah of Gujarat. Thus, on
the Raksha Bandhan day, she is being remembered.
- Humayun and Sher Shah Suri fought three battles
- In 1538, in the Battle of Chunar, Sher Shah was defeated. In this battle between Humayun and Sher Shah Suri, Humayun made a blunder
by pardoning Sher Shah.
- In 1539, in the Battle of Chausa (Bengal), Humayun was defeated and managed to escape and reached the capital Agra.
- In 1540, in the Battle of Kannauj (or Bilgram), Humayun was defeated and was dethroned by Sher Shah. Sher Shah became the king of
North and East India and ruled for 15 years.
- Initially, Humayun was given shelter by the Rajput king of Amarkot named Rana Parshad. During this time, Akbar was born
in 1542 in Amarkot to Hamida Banu Begum.
By this time, Sher Shah came to know about Humayun and warned Rajputs. Then, Humayun reached Iran,
where Safavid dynasty was ruling. King Shah Tahmasp gave shelter to Humayun.
He stayed there for more than one decade. With the
help of the military of that king, on the condition that Kandahar will be given to the Iranian king, Humayun attacked India.
In the
Battle of Sirhind, Sikandar Suri was defeated and Humayun got the kingdom again. In 1556, he fell down from the first floor of his
library (Sher Mandal) and died.
Akbar (1556-1605)
- The real name of Mughal empire ruler Akbar is Jalal-ud-din Muhammad. Three historians were there in his court, namely (i) Abul Fazl,
who wrote Akbarnama and Ain-i-Akbari, (ii) Abdul Qadir Badauni, who wrote Muntakhab-ut-Tawarikh and a chapter in Tarikh-e-Alfi and
(iii) Nizam-ud-din Ahmad, who wrote Tabaqat-e-Akbari.
- In 1555, Akbar was appointed as governor of Punjab region under the regency of Bairam Khan. When Humayun died, Akbar and Bairam
Khan were at Kalanaur (Punjab), where Akbar got coronated. Before, both of them reached Delhi and Agra, a king called Hemu captured Delhi and
Agra.
Hemu was the general and prime minister of sultan of Bihar, named Muhammad Adil Shah. By this time, Muhammad Adil Shah of Sur
dynasty was ruling Bihar region of the disintegrated Sur Empire.
- Hemu took the title of Vikramajit or Vikramaditya and ruled for 100 days. In 1556, second Battle of Panipat was fought
between Akbar and Hemu.
Hemu was defeated and Akbar came to power. During 1556-60, Bairam Khan was the de facto authority. He was called
"Khan Baba" by Akbar.
- In 1576, in the Battle of Haldighati, Sisodia king Rana Pratap Singh was defeated. It was fought between Man Singh (Akbar's agent) and Rana Pratap
Singh, who is also called Maharana Pratap.
- He built a new capital city called Fatehpur Sikri in commemoration of the victory over Gujarat. Fatehpur Sikri was the capital from
1572 to 1586.
In 1586, it was deserted because of water problem. The lake "Anoop Talab" got dried up, because of which,
Fatehpur Sikri was abandoned.
- In 1601, Salim Jahangir revolted against his father at Allahabad. Akbar deputed Abul Fazl to suppress the Salim rebellion. Abul Fazal was
assassinated by Bir Singh Dev Bundela (who built Keshava Rai Temple in Mathura), an agent of Salim.
Jahangir (1605-1627)
- Real name of Jahangir is Salim, who wrote Tuzuk-i-Jahangiri (Memories of Jahangir), his autobiography in Persian.
- During the reign of Jahangir, Khusrau(eldest son of Jahangir) rebelled against him. Guru Arjan Dev gave shelter to Khusrau.
Jahangir
captured both of them. Khusrau was blinded by Jahangir and he was put into the prison. Guru Arjan Dev was put to death.
- He made 12 ordinances (laws) for the welfare of the people like Banning of intoxicating drinks (manufacturing & consumption), Abolition of
various taxes (abwabs), Release of political prisoners, Ban of Animal killings for two days (Sunday and Thursday) in a week, Starting of
hospitals for the poor and the animals, Installation of Zanjeer-e-Adal (Bell of justice, 30 meters long chain) at Agra Fort so that anyone can
pull the chain to seek justice, etc.
- The king of England James I sent two diplomats one after the other to the court of Jahangir, namely Captain Hawkins (between 1608
and 1611) and Sir Thomas Roe (between 1615 and 1619). They came for concessions for English East India Company.
- Nur Jahan (Beauty of the World) -
- She was the most powerful woman in Mughal Empire. Original name of Nur Jahan was Mehr-un-nissa (Iranian Lady).
Jahangir married Nur
Jahan in the year 1611. She had a daughter named Ladli Begum with her first husband Sher Afgan Khan (Mughal officer of Bengal).
- She took the title of Padshah Begum. She even minted coins by her name and almost ruled the kingdom. Farmanas were also issued by Nur
Jahan.
- Jahangir gave higher positions to her kith and kin. Father of Noor Jahan, Itmad-ud-Daula was given the PM post from a petty officer.
She built the tomb of Itmad-ud-Daula at Agra. Her brother, Asaf Khan, became Mir-i-Saman (incharge of Royal Karkhanas).
Shah Jahan (1628-1658)
- Real name of Shah Jahan is Khurram. Historian Abdul Hamid Lahori, who wrote Padshahnama, gives the history about Shah Jahan in the book.
- Battles fought by Shah Jahan in Deccan -
- In 1633, Ahmadnagar was conquered and became part of Mughal empire.
- In 1636, both Bijapur and Golconda became subordinates (Kidmati) to
Mughals without any war. Even on the coins of Golconda, the name of Shah Jahan was written.
- Wars of Succession - In the last days of Shah Jahan, 4 sons fought with one another
- Dara Shikoh - He was the eldest and favourite son of Shah Jahan. He was a great scholar and an intellectual. Dara Shikoh translated
Upanishads (52 Upanishads out of 108) into Persian under the title Sirr-e-Akbar.
He also translated Bhagavad Gita and Yoga Vasishta into
Persian. He wrote number of books in Persian language like that of Majma-ul-Bahrain. He was working for Hindu-Muslim unity.
- Aurangzeb - He was the most conservative among the four sons. He was functioning as governor of Deccan.
- Murad Bakhsh - He was the governor of Gujarat and Malwa.
- Shah Shuja - He was functioning as governor of Bengal.
In 1658, there were two wars among the four brothers, namely Battle of Dharmat (Madhya Pradesh) and Battle of Samugarh. In both the battles,
Dara Shikoh was defeated and later got killed. Even Murad and Shah Shuja were killed. In 1658, Aurangzeb imprisoned his father and came to
power.
- It was Shah Jahan, who shifted the capital from Agra to Delhi after building the Red Fort in his last days.
Aurangzeb ((1658-1707)
Quiz
- Who wrote Humayun Nama, the biography of Humayun?
- Gulbadan Begum
- Abul Fazl
- Ladli Begum
- Abdul Qadir Badauni
Answer
Ans: A
- Second Battle of Panipat was fought between
- Humayun and Sher Shah Suri
- Akbar and Hemu
- Akbar and Rana Pratap
- Jahangir and Amar Singh
Answer
Ans: B
- Who translated Bhagavad Gita into Persian?
- Shah Shuja
- Murad Bakhsh
- Alamgir I
- Dara Shikoh
Answer
Ans: D



